Talk Overview
In this talk about eyepieces, Stephen Ross gives a short description of what is in an eyepiece and how it works.
Speaker Bio
Steve Ross

Stephen Ross is the General Manager of Product and Marketing at Nikon Instruments. He is also very involved in teaching microscopy at the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole and at the Bangalore Microscopy Course at the National Centre for Biological Sciences. Continue Reading
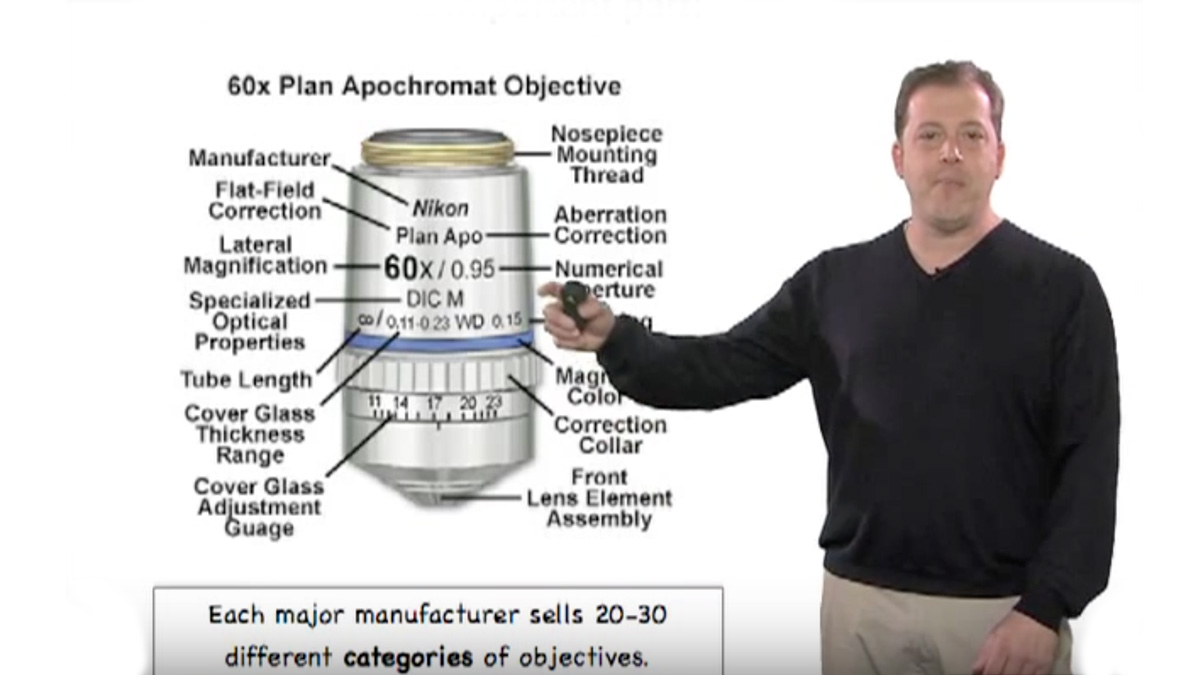






Leave a Reply